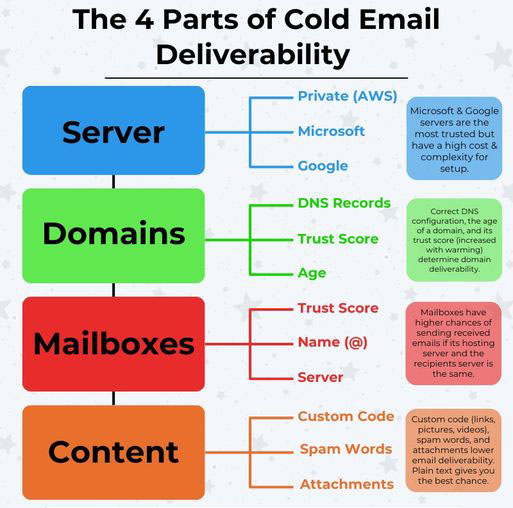
Here are the 4 parts of cold email (& how to optimize them):
1. Server
Your server is where you host your domains. This can be:
Private (AWS)
Microsoft
Google
Google & Microsoft have the highest trust, but they come with higher costs & complexity.
On the other hand, private servers (e.g., ReachInbox) can be set up quickly and affordably, but… these have low trust and are more likely to be blacklisted.
=> If you’re new to deliverability, avoid private servers.
2. Domains
Your domains are where you host your mailboxes.
What affects domain deliverability?
DNS Records
Trust Score
Age
For DNS records, you want the following setup (use EasyDmarc):
BIMI (If you can)
DMARC
DKIM
SPF
Domains also have an rDns record based on their origin.
For the highest trust, get domains from GoDaddy.
Get domains that are at least 30 days old (the older, the better).
This impacts the trust score, which is increased by warming.
3. Mailboxes
Mailboxes send & receive emails based on their server.
Most B2B mailboxes are either Google or Microsoft.
If you send an email from a Google-based mailbox to a Google-based mailbox, you have a high chance of getting through.
But if you send the same email from an AWS-based mailbox, you’re more likely to end up in spam.
For the best deliverability: Get both Google & Microsoft mailboxes and enable provider matching.
4. Content
This is the actual content & copy in the email.
Generally, the more you add to your email, the lower its deliverability.
Avoid any:
Links
Videos
Images
Custom code of any kind
For the text you include, use MailMeteor to catch any flaggable spam words.